Admin Custom Entities
If you have created a brand new entity in your Broadleaf application and wish to manage it through the Admin, you can follow these steps below to easily create sections and maintenance pages using only annotations.
This guide assumes that your project structure follows the structure of the Heat Clinic Demo Site. (i.e. 3 maven modules
admin,site, andcorewhere bothadminandsitedepend oncore)
Managing a custom entity in the Broadleaf Admin
Create your custom classes. Here is a very simple implementation of one:
@Entity @Table(name="MY_CUSTOM_CLASS") @Inheritance(strategy = InheritanceType.JOINED) @Cache(usage = CacheConcurrencyStrategy.READ_WRITE, region="blStandardElements") @AdminPresentationClass(friendlyName = "MyCustomClassImpl") public class MyCustomClassImpl implements MyCustomClass { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; @Id @GeneratedValue(generator = "MyCustomClassId") @GenericGenerator( name="MyCustomClassId", strategy="org.broadleafcommerce.common.persistence.IdOverrideTableGenerator", parameters = { @Parameter(name="segment_value", value="MyCustomClassImpl"), @Parameter(name="entity_name", value="com.mycompany.sample.domain.MyCustomClassImpl") } ) @Column(name = "MY_CUSTOM_CLASS_ID") protected Long id; @Column(name = "NAME", nullable = false) @AdminPresentation(friendlyName = "MyCustomClassImpl_name", order = 1, prominent = true, gridOrder = 1) protected String name; @Override public Long getId() { return id; } @Override public void setId(Long id) { this.id = id; } @Override public String getName() { return name; } @Override public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
For this example, we will place this entity in our core project:
Note: You may also wish to Internationalize some of the Friendly Names on your entity. You can do so by adding it to your
messages-admin.propertiesfiles accordingly.
Make sure your classes are component-scanned. In this example, make sure your
coreproject has in itsapplicationContext.xml:<context:component-scan base-package="com.mycompany.sample" />
Make sure your custom class is registered with the persistence unit in
core’spersistence-core.xmlfile:<persistence-unit name="blPU" transaction-type="RESOURCE_LOCAL"> <non-jta-data-source>jdbc/web</non-jta-data-source> <class>com.mycompany.sample.domain.MyCustomClassImpl</class> <exclude-unlisted-classes/> </persistence-unit>
Create Admin Permissions for your new entity. For this example, we will create a SQL file to load these permissions:
/sql/load_my_custom_class_admin_security.sql:
-- Create new custom module
INSERT INTO BLC_ADMIN_MODULE (ADMIN_MODULE_ID, NAME, MODULE_KEY, ICON, DISPLAY_ORDER) VALUES (1000, 'MyCustomModule','MyCustomModule', 'icon-globe', 1);
-- Create Admin permissions and entity permissions for your new entity
INSERT INTO BLC_ADMIN_PERMISSION (ADMIN_PERMISSION_ID, DESCRIPTION, NAME, PERMISSION_TYPE, IS_FRIENDLY) VALUES (1000,'Read MyCustomClass','PERMISSION_READ_MY_CUSTOM_CLASS', 'READ', FALSE);
INSERT INTO BLC_ADMIN_PERMISSION (ADMIN_PERMISSION_ID, DESCRIPTION, NAME, PERMISSION_TYPE, IS_FRIENDLY) VALUES (1001,'All MyCustomClass','PERMISSION_ALL_MY_CUSTOM_CLASS', 'ALL', FALSE);
INSERT INTO BLC_ADMIN_PERMISSION_ENTITY (ADMIN_PERMISSION_ENTITY_ID, CEILING_ENTITY, ADMIN_PERMISSION_ID) VALUES (1000, 'com.mycompany.sample.domain.MyCustomClass', 1000);
INSERT INTO BLC_ADMIN_PERMISSION_ENTITY (ADMIN_PERMISSION_ENTITY_ID, CEILING_ENTITY, ADMIN_PERMISSION_ID) VALUES (1001, 'com.mycompany.sample.domain.MyCustomClass', 1001);
-- Friendly permissions
INSERT INTO BLC_ADMIN_PERMISSION (ADMIN_PERMISSION_ID, DESCRIPTION, NAME, PERMISSION_TYPE, IS_FRIENDLY) VALUES (1002,'View My Custom Class','PERMISSION_MY_CUSTOM_CLASS_VIEW', 'READ', TRUE);
INSERT INTO BLC_ADMIN_PERMISSION_XREF (ADMIN_PERMISSION_ID, CHILD_PERMISSION_ID) VALUES (1002, 1000);
INSERT INTO BLC_ADMIN_PERMISSION (ADMIN_PERMISSION_ID, DESCRIPTION, NAME, PERMISSION_TYPE, IS_FRIENDLY) VALUES (1003,'Maintain My Custom Class','PERMISSION_MY_CUSTOM_CLASS_ALL', 'ALL', TRUE);
INSERT INTO BLC_ADMIN_PERMISSION_XREF (ADMIN_PERMISSION_ID, CHILD_PERMISSION_ID) VALUES (1003, 1001);
-- Add Role Permission XREF to the All Permission
INSERT INTO BLC_ADMIN_ROLE_PERMISSION_XREF (ADMIN_ROLE_ID, ADMIN_PERMISSION_ID) VALUES (-1,1003);
-- Mapping sections and permissions
INSERT INTO BLC_ADMIN_SECTION (ADMIN_SECTION_ID, DISPLAY_ORDER, ADMIN_MODULE_ID, NAME, SECTION_KEY, URL, CEILING_ENTITY) VALUES (1000, 1, 1000, 'My Custom Class', 'MyCustomClass', '/my-custom-class', 'com.mycompany.sample.domain.MyCustomClass');
INSERT INTO BLC_ADMIN_SEC_PERM_XREF (ADMIN_SECTION_ID, ADMIN_PERMISSION_ID) VALUES (1000,1002);
INSERT INTO BLC_ADMIN_SEC_PERM_XREF (ADMIN_SECTION_ID, ADMIN_PERMISSION_ID) VALUES (1000,1003);
When you're done make sure that it gets loaded properly, in this example you can add it to development-shared.properties to have it automatically loaded during development.
blPU.hibernate.hbm2ddl.import_files=/config/bc/sql/load_admin_permissions.sql,\
/config/bc/sql/load_admin_roles.sql,\
/config/bc/sql/load_admin_menu.sql,\
/config/bc/sql/load_menu_admin_security.sql,\
/sql/load_my_custom_class_admin_security.sql,\
/sql/load_admin_users.sql,\
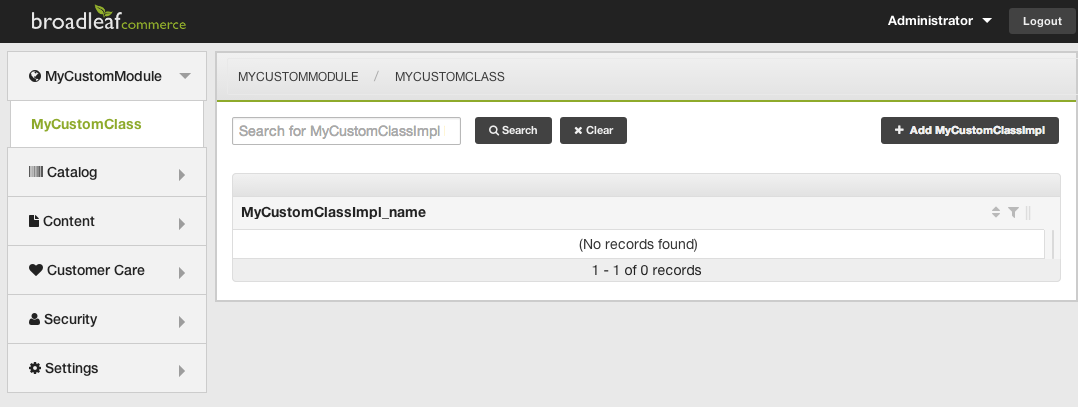
- Check the Admin For you New Entity
That's it! At this point, your admin Module and Section should be generated appropriately and you should be able to manage your new entity in the Admin.